

Vacuum Heat Treatment Furnace
Vacuum Sintering Furnace
Vacuum Brazing Furnace
(The article comes from the Internet. If reprinting is not allowed, please contact our company to delete it.)
Please send us your inquiry about the customization of other furnace types or related questions about vacuum furnace. We will reply you immediately. Thank you.
 Downloads
Downloads
All documents in the overview
 News & Press
News & Press
All news at a glance
 Request
Request
Send us a message
Email: contact@vacfurnace.com
Tel : +86-21-50878190
Wechat : 2210154395
Address: NO.1299, XinJinQiao Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai, China.
Copyright © 2010-2021 Shanghai Gehang Vacuum Technology Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
metal injection molding
A metal MIM piece like an injection molding tool to help you understand metal injection molding
MIM is a metal processing and forming process
MIM is the short for Metal injection Molding.It is a molding method in which metal powder and its binder plasticized mixture are injected into the model.It is the shape required by first mixing the selected powder with the binder, then pelleting the mixture and injecting it.
MIM process steps
The MIM process combines the flexibility of injection molding design with the high strength and integrity of precision metals to achieve a low-cost solution for extremely complex geometric components.The MIM process is divided into four unique processing steps (mixing, forming, degreasing and sintering) to realize the production of parts and determine whether surface treatment is required for product characteristics.
hybrid

The fine metal powder is mixed with thermoplastic and paraffin binder in precise proportions.The mixing process is carried out in a special mixing equipment and heated to a certain temperature to melt the binder.In most cases, mixing is done mechanically until the metal powder particles are evenly coated with the binder and cooled to form particles (called feedstock) that can be injected into the mold cavity.
Molding
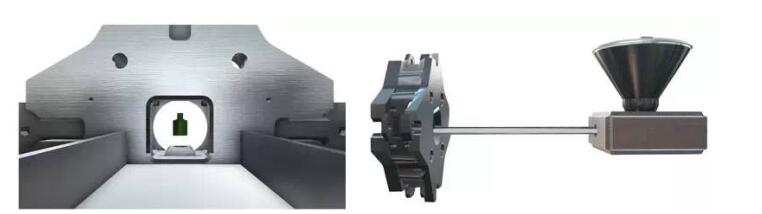
The equipment and techniques of injection molding are similar to injection molding.The granular material is fed into the machine to heat and injected into the mold cavity at high pressure.This part forms (Green part) after cooling and demodulates. The whole process can only be carried out when the binder is melted (fully fused with the metal powder) at about 200° C. The mold can be designed with multiple cavities to increase productivity.Cavity size design should consider the shrinkage of metal parts during sintering.The change in shrinkage of each material is precise and known.
Debinding
Degreasing is the process of removing the binder from the molded parts.This process is usually done in several steps.Most of the binder is removed before sintering, the residual part can support the parts into the sintering furnace.
Degreasing can be done in a variety of ways, depending on the ingredients of the feed, the brand.The most commonly used methods are catalytic degreasing and solvent extraction.The degreased parts are semi-permeable and the residual binder is easily volatilized during sintering.
Sintering
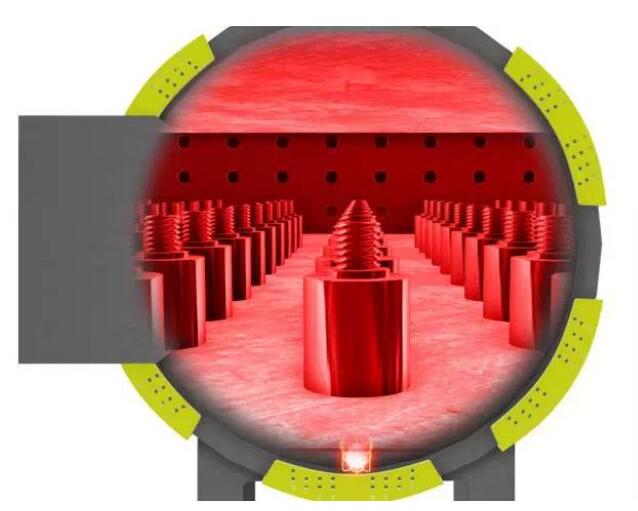
The degreased parts are put into a high temperature, high pressure controlled furnace.The unit is heated slowly, protected by gas, to remove residual adhesive.After the binder is completely removed, the component is heated to a very high temperature, and the gaps between the particles disappear due to particle fusion.The component directionally shrinks to its design size and transforms into a compact solid.For most materials, the typical sintering density is theoretically greater than 97%.The high sintering density makes the properties similar to those of forged materials.
Surface treatment
Some parts may require surface treatment after sintering, depending on specific requirements.Heat treatment can improve the physical properties of metals.Electroplating and coating can be applied to high density materials.Provide welding or cooling treatment technology.
MIM products typically have the following features
complexity
The MIM, like injection molding, has no limits to shape design.Because the MIM is a molding process, additional product features do not add cost, making the MIM an ideal way to combine individual parts into multifunctional products.The MIM design rules are very similar to injection molding and thus apply to almost all products.
Precision
The reference design for the accuracy of MIM net shaping is usually ± 0.5% of the size.Some features of the net molding up to ±0.3%.As with other technologies, the higher the accuracy requirement, the higher the cost, so modest tolerance requirements are encouraged where quality permits.Tolerances that cannot be achieved in a single MIM formation can be achieved with the aid of surface treatment.
Weight and dimensions
The MIM is especially suitable for parts weighing less than 100g, less than 50g is the most economical.However, parts weighing up to 250g can also be handled.The main cost of the MIM process is raw materials, so MIM USES new technology to minimize the weight of components.As with plastic products, the weight of components can be reduced through cores and supports without compromising product integrity.The MIM stands out in terms of very small and micro components, and it is possible to weigh less than 0.1 grams.Weight is not a limiting factor and products over 250mm in length can be handled.
Thin,
Wall thickness less than 6 mm is best for MIM.Thicker walls are also available, but the cost increases due to longer processing times and the addition of additional materials.In addition, a very thin wall less than 0.5 mm can also be realized for MIM, but it has high requirements for design
Production
The MIM is a highly flexible process, and yields that require thousands to millions of dollars a year can be achieved very economically.Like casting and injection parts, MIM requires customers to invest in molds and tools, so for small batches of products, cost estimates are often influenced.
The raw material
The MIM can handle a wide range of materials, including ferroalloys, superalloys, titanium alloys, copper alloys, refractory metals, hard alloys, ceramics, and metal-matrix composites.Although non-ferrous aluminum and copper alloys are technically feasible, they are usually treated in other, more economical ways, such as die casting or machining.
MIM design guidance
MIM is widely applied to the automotive, medical, electronics, industrial, consumer and other various industries, including auto parts products involving, aerospace equipment, mobile phones, dental instruments, electronic radiator and seal packaging, electronic connectors, hardware, industrial tools, fiber optic connectors, spray system, disk drive, medical equipment, portable power tools, surgical instruments, sports equipment and so on.
The most important parts of the MIM production line are feeding, injection machines, and the selection of degreasing and vacuum sintering furnaces.
SIMUWU catalytic degreasing furnace USES nitric acid or oxalic acid to remove POM by the degreasing method of nitrogen atmosphere charging and washing, which is safe and reliable. Compared with solvent degreasing, it has the advantages of larger yield and smaller performance.
The following are the degreasing furnace specifications of different specifications:
In addition, the SIMUWU vacuum sintering furnace has nitrogen, argon and hydrogen gas in different atmospheres, which can be customized according to different processes.
The use temperature of MIM sintering generally does not exceed 1300℃, and the equipment with the highest temperature of 1400℃ can be designed.Or customize SIMUWU standard RVS-M series vacuum debinding and sintering furnace.
dimension
(mm)
(C)
pressure
(Pa)
rising rate
(pa/h)
uniformity
(C)
capacity
(kg)
Edited by: Lucky Hu;
Copyright: SIMUWU Vacuum Furnace
Related products:
MIM sintering Furnace.
Catalytic debinding furnace
Vacuum debinding&sintering furnace